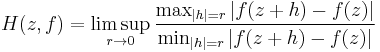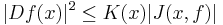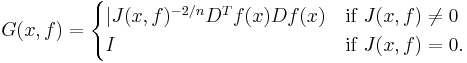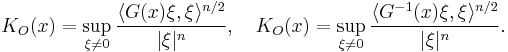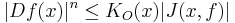Distortion (mathematics)
In mathematics, the distortion is a measure of the amount by which a function from the Euclidean plane to itself distorts circles to ellipses. If the distortion of a function is equal to one, then it is conformal; if the distortion is bounded and the function is a homeomorphism, then it is quasiconformal. The distortion of a function ƒ of the plane is given by
which is the limitting eccentricity of the ellipse produced by applying ƒ to small circles centered at z. This geometrical definition is often very difficult to work with, and the necessary analytical features can be extrapolated to the following definition. A mapping ƒ : Ω → R2 from an open domain in the plane to the plane has finite distortion at a point x ∈ Ω if ƒ is in the Sobolev space W1,1
loc(Ω, R2), the Jacobian determinant J(x,ƒ) is locally integrable and does not change sign in Ω, and there is a measurable function K(x) ≥ 1 such that
almost everywhere. Here Df is the weak derivative of ƒ, and |Df| is the Hilbert–Schmidt norm.
For functions on a higher-dimensional Euclidean space Rn, there are more measures of distortion because there are more than two principal axes of a symmetric tensor. The pointwise information is contained in the distortion tensor
The outer distortion KO and inner distortion KI are defined via the Raleigh quotients
The outer distortion can also be characterized by means of an inequality similar to that given in the two-dimensional case. If Ω is an open set in Rn, then a function ƒ ∈ W1,1
loc(Ω,Rn) has finite distortion if its Jacobian is locally integrable and does not change sign, and there is a measurable function KO (the outer distortion) such that
almost everywhere.
See also
References
- Iwaniec, Tadeusz; Martin, Gaven (2001), Geometric function theory and non-linear analysis, Oxford Mathematical Monographs, The Clarendon Press Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-850929-5, MR1859913.
- Reshetnyak, Yu. G. (1989), Space mappings with bounded distortion, Translations of Mathematical Monographs, 73, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, ISBN 978-0-8218-4526-4, MR994644.